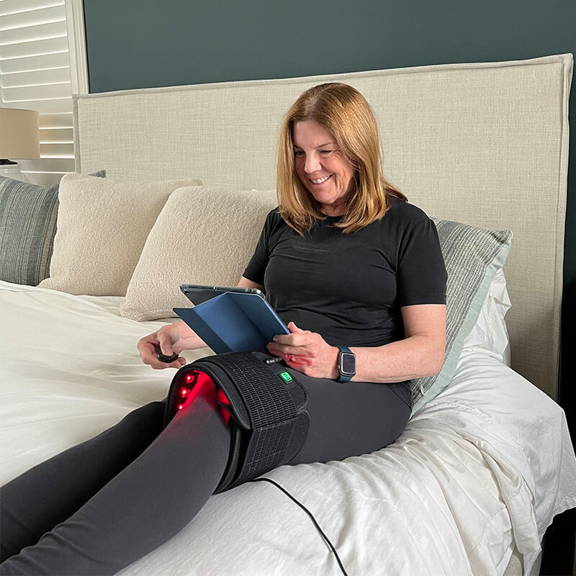
Deep healing red light therapy has been shown to restore normal mitochondrial functioning through a process known as photobiomodulation. When cells are exposed to red light, light-absorbing molecules called chromophores within the mitochondria, such as cytochrome c oxidase, are activated. This activation triggers a series of intracellular events, including the enhancement of electron transport chain activity and increased mitochondrial membrane potential. These effects lead to improved ATP production, enhanced cellular respiration, and optimized mitochondrial functioning. This promotes the synthesis of proteins, DNA, and other molecules necessary for nerve growth and repair. Red light therapy also helps to reduce oxidative stress by promoting the production of antioxidants and scavenging reactive oxygen species, which can damage mitochondria. By restoring normal mitochondrial functioning, red light therapy provides cells with the energy and resources necessary for optimal cellular activities and overall health.
“The laser causes hyperpolarization of the cell membrane and activation of the resynthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which provides free energy for the regenerative bioprocesses through hydrolysis.” National Library of Medicine, 2021